Table of Contents
What is business process automation?
How does business process automation work?
What business processes can be automated?
How to automate business tasks?
How to choose the right task automation tool?
How does business process automation software work?
Automation in action: an example of the advantages of automation
Challenges of business process automation
Create an edge by leveraging the advantages of automation
Introduction to automation
Whether you are a start-up founder or a CIO at an MNC, it’s certain that your teams are spending more than a couple of hours each day on administrative tasks that are integral to your business. As important as these tasks are, they can be automated to save your employees’ time and utilise it better.
There are numerous advantages to automation in terms of the time saved and improved productivity. Automation is critical to managing, changing, and updating not only your IT infrastructure, but the way your business operates through its processes.
What is business process automation?
Business process automation (BPA) is simplifying and performing repetitive tasks without the need for human intervention. What this translates to is a highly motivated team that’s freed up for strategic and creative work, and businesses that are ready to scale up through error-free processes.
Businesses are adapting to disruption in various domains by automating processes across several core and support verticals, ranging from inventory management, payload and scheduling to employee management, customer engagement, sales, and marketing.
How does business process automation work?
Not only does an automation tool streamline all these tasks, but when it is connected with other tools, it can gather the right data needed to perform tasks correctly. It can also work seamlessly with your internal platforms and tools, often without any need for change in existing workflows or project execution plans that are underway.
What business processes can be automated?
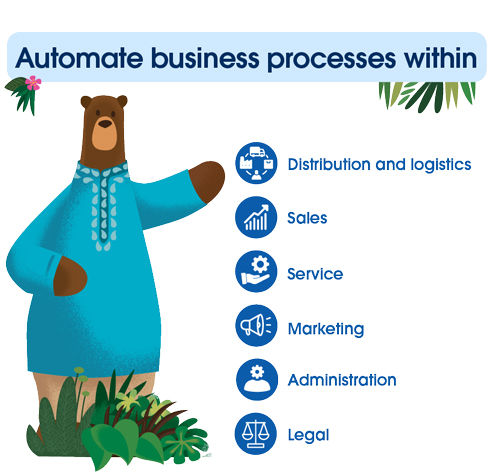
Below are some examples of business processes that can be automated in:
Distribution: You can automatically create transportation routes, calculate order volumes, track and log the movement of goods, and do more.
Logistics: Automation tools can help with labelling and managing inventories, as well as setting up alerts on items that are running low.
Sales: Automation helps simplify sales teams' efforts around lead management, tracking opportunities, prospect follow-ups, reporting, configuring, pricing, and quoting, etc.
Administration: Automation can streamline time-consuming processes like payroll creation and management, processing salaries and taxes.
Marketing: Automate your marketing campaigns, newsletter sends, social media posting and ad campaigns using marketing automation tools. Automation can help easily scale marketing campaigns and maximise their impact.
Customer service: Automation can enable service teams to consolidate service requests, feedback, common queries, etc. from different touchpoints onto a single platform. You can also automate customer engagement and case resolution through tools like chatbots and auto reply emails, among other things.
Legal: Automation tools can help secure legal agreements, deploy contract workflows, review thousands of documents with unstructured data, manage risk and compliance, etc.
Why is automation important?
While getting an order's details wrong or entering incorrect data are problems that can be resolved, it takes up valuable time. Manual data collection can cost businesses a lot of time and money.
If used correctly, a well-designed automation tool can ensure that a business becomes more profitable for those running it and more convenient for those using its services. The automation of redundant tasks like data entry also ensures the accuracy of data.
At the end of the day, process automation enables organisations to do more in less time. By saving time on repetitive, manual tasks, teams can focus on more value-added work, like building customer relationships.
How to automate business tasks?
Identifying fundamental and repetitive tasks is a prerequisite to incorporating automation in your business process. For instance, recognising whether it is possible to create a work order automatically once a project has been confirmed.
It's best to begin your automation journey with something small yet impactful. This helps you conserve resources while learning about which aspects of your business need to be automated. Carry those lessons forward, taking an incremental approach.
A highly evolved approach for automating business processes is to view functionalities via a “systems thinking” lens. Systems thinking looks at individual decisions and the consequences they have on the entire ecosystem of the business or organisation, internally and externally. For example, you can look at the current sales processes and suggest how automating the fulfillment or invoicing processes can impact your business.
This broader view allows CIOs and project managers to assess where automation should be deployed, what tools make the most sense for different activities, and what processes can be redesigned for simplicity.
How to choose the right task automation tool?
1. Outlining the processes that need automation
2. Doing your research
3. Considering the tool's scalability capabilities
Want to create custom automated processes for your business?
7 advantages of automation
1. Maximises resources:
2. Frees up time:
3. Eliminates errors:
4. Converts data into insights:
5. Increases efficiency:
6. Enables better customer service:
7. Boosts scalability:

How does business process automation software work?
BPA is available in different formats for a range of functionalities. While it is primarily a software application, it can also involve the use of robotics. These tools turn manual actions into workflows that require minimal to no human intervention.
Depending on your needs, you can get automation software for specific functions (like marketing) or a CRM with automation capabilities to streamline business processes across functions. Task automation tools offered by companies such as Salesforce do not even require coding. These tools are designed keeping business users in mind. But you can also use its pro-code tools for finer customisation.
Point-and-click features help automate tasks for consistency and timeliness. Ultimately, process automation enables organisations to do more with less in lesser time.
Automation in action: an example of the advantages of automation
Let’s take the example of an IT company that provides customised tech solutions across the logistics, transportation, and storage industries. If this company has to generate leads for acquiring new customers and target existing clients, this will involve a series of tasks around prospect data entry, data segmentation, prospect allocation, as well as a full range of marketing and social media campaigns.
Using traditional methods for following up with qualified leads, and monitoring ad campaign performance would involve many team members spending hundreds of hours poring over data and responding to sales queries from customers. As the business grows and the volume of inquiries increases, the response time will also increase.
This is where a marketing automation application can transform how your business captures, manages and nurtures leads, all the way to content management, CRM integration, analytics, and reporting.
Challenges of business process automation
Deploying a highly efficient business process automation tool does come with a set of challenges, chiefly the human resistance to change in the status quo. There are also concerns about job redundancies and lack of skilled resources who can adapt to the change.
Let’s take a look at 4 challenges businesses may face when opting for BPA:
1. Gauging the long-term impact of automation
Set automation targets for each department and assess whether software, AI, or technology platforms can optimise your delivery times, lead generation time or improve employee productivity.
2. Budget constraints
3. Quality control after automation
4. Employee onboarding while automation is in progress
As with any change in the workforce, the deployment of an updated technology brings with it resistance and confusion for employees. Conduct training sessions that help teams to understand the purpose of the BPA, its functionality, and how the workflow is going to change for the better for them.
CIOs and senior managers can also consider assigning a member from each function as a change ambassador. These POCs can help teams speed up adoption and allay concerns around becoming redundant.
Create an edge by leveraging the advantages of automation
To sum it up, the goal of any business or start-up should be to automate as many repetitive tasks as required, so that it allows your workforce to focus on strategic activities.
For customers, automation tools make interactions seamless, intuitive, and delightful. This increases customer satisfaction, leading to customer loyalty and developing a strong bond between customers and the company.
For business owners, automation tools provide smoother workflows and easier management of tasks. This reduces stress on employees, cuts procurement costs and intensive human resources capital, and helps the business to function smoothly.
All these advantages make automation one of the most important business tools that companies can adopt today.





